High blood pressure – also called hypertension is one of the most common health problems in the world. Many people have it without even knowing, because it often causes no warning signs at first. But even when it’s silent, it can damage the heart, brain, kidneys, and blood vessels.
Think of your blood vessels like garden hoses. When the pressure is normal, the hose works well. But if the pressure becomes too strong, the hose can get damaged, leak, or burst. That is what happens inside the body when blood pressure stays high for too long.
This guide explains high blood pressure in simple language, with all the essential details you need to stay healthy.
What Is Blood Pressure? (Explained Simply)
Blood pressure is the force your blood makes as it pushes through your blood vessels.
It has two numbers:
-
Systolic (top number): Pressure when your heart squeezes.
-
Diastolic (bottom number): Pressure when your heart relaxes.
Example: 120/80 mmHg.
Stages of High Blood Pressure
Here are the official stages explained clearly:
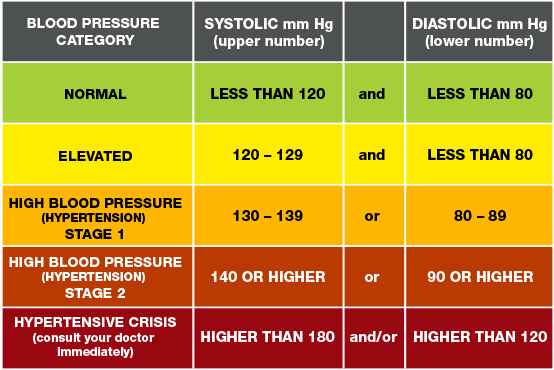

1. Normal Blood Pressure
-
Less than 120/80
This is healthy and safe. Your heart and blood vessels are not under stress.
2. Elevated Blood Pressure
-
120–129 / below 80
Not yet hypertension, but warning stage. Lifestyle changes are needed immediately.
3. Stage 1 High Blood Pressure
-
130–139 / 80–89
Doctors may recommend lifestyle changes and sometimes medications.
4. Stage 2 High Blood Pressure
-
140 or higher / 90 or higher
Serious stage. Medication is almost always needed to control it.
5. Hypertensive Crisis (Emergency)
-
180+ / 120+
Causes of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can develop slowly over many years. Common causes include:
1. Genetics
If your parents or siblings have high blood pressure, your risk is higher.
2. Unhealthy Diet
Too much:
-
Salt
-
Fried food
-
Fast food
-
Processed snacks
-
Sugary drinks
3. Obesity and Belly Fat
Abdominal fat increases pressure on blood vessels.
4. Stress
Chronic stress keeps your body in “fight-or-flight mode,” raising blood pressure.
5. Smoking
Nicotine tightens blood vessels and increases pressure.
6. Alcohol
Too much alcohol raises blood pressure and damages the heart.
7. Lack of Exercise
The heart becomes weaker and blood flow becomes less efficient.
8. Kidney Problems
Kidneys help control fluid balance and pressure.
9. Horonal Conditions
Examples: thyroid disease, adrenal tumors.
Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is often called the silent killer because many people feel nothing.
But when symptoms appear, they may include:
General Symptoms
-
Headache
-
Dizziness
-
Blurry vision
-
Nosebleeds
-
Chest pain
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fatigue
-
Irregular heartbeat
Symptoms in Men
-
Chest tightness
-
Low libido or erectile issues
-
More sweating
-
Feeling hot or flushed
-
Anxiety during pressure spikes
Symptoms in Women
-
Head pressure
-
Swelling in legs
-
Extreme tiredness
-
Hot flashes
-
Neck or shoulder pain
Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is often called the silent killer because many people feel nothing.
But when symptoms appear, they may include:
General Symptoms
-
Headache
-
Dizziness
-
Blurry vision
-
Nosebleeds
-
Chest pain
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fatigue
-
Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath during routine activities
Why Sweating Happens with High Blood Pressure
Sweating can occur because:
-
The heart is working too hard
-
Stress hormones surge
-
Blood pressure spikes suddenly
-
Anxiety kicks in during a pressure rise
This is why some people feel sweaty or shaky during an episode.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus n
How Stress Affects Blood Pressure
Stress makes your body release cortisol and adrenaline—chemicals that:
-
Make your heart beat faster
-
Tighten your blood vessels
-
Increase blood flow force
-
Raise blood pressure temporarily
When stress happens every day (work, family, money worries), the temporary rises become permanent, leading to hypertension.ec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Complications: Stroke and Heart Attack
High blood pressure damages blood vessels over time—making them weak, stiff, or narrow.
1. Stroke


High blood pressure can cause:
-
A vessel in the brain to burst (hemorrhagic stroke)
-
A clot to block blood flow to the brain (ischemic stroke)
Symptoms are sudden:
-
Weakness on one side
-
Trouble talking
-
Severe headache
-
Confusion
This is a medical emergency.
2. Heart Attack

When blood pressure stays high:
-
Blood vessels supplying the heart get narrow
-
Heart muscles receive less oxygen
-
A blockage forms → heart attack
Symptoms:
-
Chest pain or pressure
-
Pain in jaw, arm, or back
-
Shortness of breath
-
Sweating
-
Nausea
Simple Ways to Prevent or Control High Blood Pressure
-
Eat low-salt foods
-
Get 30 minutes of exercise daily
-
Lose excess weight
-
Stop smoking
-
Reduce alcohol intake
-
Get good sleep
-
Drink enough water
-
Manage stress through meditation or deep breathing
-
Check blood pressure regularly
Medications for High Blood Pressure (With Simple Explanations)
Doctors prescribe one or more medicines depending on your stage.
1. Diuretics (“Water Pills”)
Help kidneys remove extra salt and water.
Examples: Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), Chlorthalidone
Side effects: Frequent urination, dizziness, low potassium.
2. ACE Inhibitors
Relax blood vessels.
Examples: Lisinopril, Enalapril
Side effects: Dry cough, dizziness, high potassium.
3. ARBs
Similar to ACE inhibitors but without the cough.
Examples: Losartan, Valsartan
Side effects: Dizziness, high potassium.
4. Calcium Channel Blockers
Slow the heart and relax blood vessels.
Examples: Amlodipine, Diltiazem
Side effects: Swelling in legs, headache, flushing.
5. Beta Blockers
Reduce heart rate and workload.
Examples: Metoprolol, Atenolol
Side effects: Fatigue, depression, cold hands/feet.
6. Combination Medications
A mix of two or three drugs in one pill.
The Best Diet for High Blood Pressure: The DASH Diet
The DASH diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) is proven to lower blood pressure naturally.
Foods to Eat More Of
-
Fruits
-
Vegetables
-
Whole grains
-
Beans
-
Nuts and seeds
-
Lean meat, fish, poultry
-
Low-fat dairy
-
Olive oil
Foods to Avoid or Reduce
-
Salt (choose less than 2,300 mg per day)
-
Fast foods
-
Processed snacks
-
Canned soups
-
Soda and sugary drinks
-
Red meat
-
Butter and high-fat dairy
Simple DASH Meal Example
-
Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries
-
Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with olive oil
-
Dinner: Baked salmon, steamed broccoli, brown rice
-
Snack: Almonds or a banana
Final Thoughts
High blood pressure is serious but manageable. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatments, and lifestyle changes can help you stay healthy and prevent life-threatening complications like stroke or heart attack.
By eating wisely, staying active, managing stress, and taking medications when needed, anyone can keep their blood pressure under control and protect their long-term health.